AI Heavyweights: NVIDIA Vs AMD in the Boxing Ring
The introduction of AI PCs marks a new era in personal computing. AI is no longer hype; the first real competition has just begun at the high-end AI chips for data center servers. In the AI ring, on one corner, we have AMD! Known for its prowess as a CPU manufacturer, AMD has shown remarkable growth, boasting a nearly 700% return over the past five years. With a projected stock price target of $284.55 for 2025, AMD is ready to take on any challenger with its cutting-edge technology! And in another corner, standing tall with an established position and continuous innovation, we have NVIDIA (NVDA)! This titan of AI hardware development has seen a staggering over 400% increase in revenue in the past five years. NVIDIA's relentless drive and groundbreaking advancements keep it at the forefront of the AI industry, making it a formidable opponent in this bout!"
At present [June of 2024), NVIDIA holds a dominant position with about 80% market share in the AI chip market, thanks to its flagship AI GPU, the H100, giving it a significant lead over competitors. In this article, we will compare AI chips, ultra-speed networking, and strategic partnerships. In the era of digital transformation, having extensive partnerships with the right providers and OEMs offers a strategic advantage over rivals. Strong collaboration can be the competitive edge that keeps a company at the forefront of the competition.
Real-Time Stock Price Charts for NVIDIA and AMD
Financial Strengths and Performance [up to June 2024]
Let's dive into the analysis of their financial strengths and performance, focusing on growth trends.
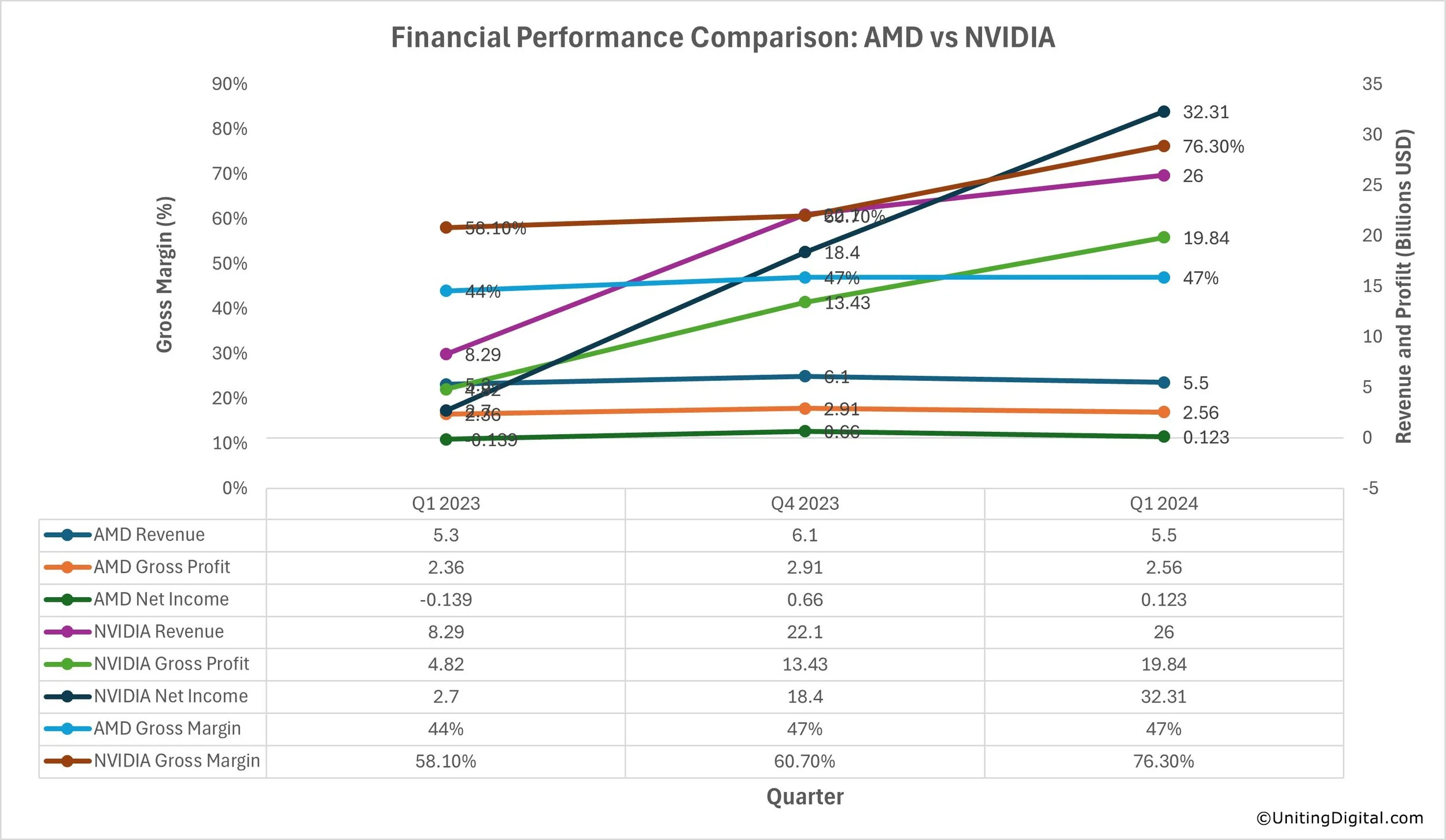
A Financial Performance Comparison: AMD vs NVIDIA
AMD:
Revenue: $5.5B (Q1 2024), $5.3B (Q1 2023), $6.1B (Q4 2023).
Gross Profit: $2.56B (Q1 2024), $2.36B (Q1 2023), $2.91B (Q4 2023).
Net Income: $0.123B (Q1 2024), -$0.139B (Q1 2023), $0.667B (Q4 2023).
Gross Margin: 47% (Q1 2024), 44% (Q1 2023), 47% (Q4 2023).
NVIDIA:
Revenue: $26B (Q1 2024), $8.29B (Q1 2023), 22.1B (Q4 2023).
Gross Profit: $19.84B (Q1 2024), $4.82B (Q1 2023), $13.43B (Q4 2023).
Net Income: $32.31B (Q1 2024), $2.7B (Q1 2023), $18.4B (Q4 2023).
Gross Margin: 76.3% (Q1 2024), 58.1% (Q1 2023), 60.7% (Q4 2023).
Both AMD and NVIDIA have demonstrated significant financial performance. Still, NVIDIA's financial strength shows impressive revenue growth and gross margins, reflecting its dominant market position, especially driven by its AI products and data center solutions. Additionally, NVIDIA consistently maintains higher gross margins than AMD, reflecting its strong pricing power and efficient cost management. From a financial performance perspective, NVIDIA's net income shows its profitability, significantly outperforming AMD.
Which Chips offer the better AI and HPC performance?
The AMD MI300X offers higher memory capacity, better bandwidth, and superior energy efficiency with a strong price-performance ratio. In contrast, NVIDIA's H200 excels in peak performance with robust software ecosystem support, despite higher power consumption and cost. While AMD's software support has lagged, the ROCm 6 framework is closing the gap with significant improvements. NVIDIA, however, maintains a major advantage for developers and researchers due to its well-established software ecosystem. At Computex 2024 in Taiwan, AMD introduced the MI400 series, set for release in 2026, based on the new "Next" architecture. NVIDIA unveiled its Rubin AI chip platform, which will also launch in 2026 and include GPUs, CPUs, and networking chips. AMD shared details about its new neural processing units (NPUs) for AI PCs. Earlier at Microsoft Build, an annual conference for software engineers and developers, NVIDIA was mentioned as a full-stack partnership from Blackwell to Omniverse, while AMD was also mentioned as an expanded partnership in the ND MI300X V5 accelerator.
Ultra-Speed Networking for HPC and AI Workloads
Modern AI and HPC workloads require ultra-speed networks to handle continuous computing, synchronization, and communication between various process nodes. Conventional networks fall short of these needs due to their limited speed and capacity since handling AI workloads involves a continuous computing loop.
AMD's Approach with UALink and Ultra Ethernet:
To address this challenge, AMD and seven other companies in the UALink consortium (Microsoft, Broadcom, Cisco, Google, HPE, Intel, and Meta) have developed an open standard specification. This promotes interoperability and efficiency in AI data centers, enhancing flexibility and integration. To implement UALink, the Ultra Ethernet Consortium helps create a robust and efficient networking infrastructure that supports the demanding requirements of AI and HPC applications, facilitating UALink deployment.
NVIDIA's Spectrum-X Platform:
NVIDIA's Spectrum-X is an Ethernet-based networking platform designed to improve AI cloud performance and efficiency. It integrates the Spectrum-4 Ethernet switch with the BlueField-3 DPU, offering up to 1.7x better AI performance and power efficiency. The platform supports 256 200Gb/s ports with a single switch, or up to 16,000 ports in a two-tier leaf-spine topology, ensuring high scalability for AI workloads. Spectrum-X seamlessly works with NVIDIA's AI software stack, including tools like SONiC, Cumulus Linux, NetQ, and DOCA, enabling faster deployment and optimization. In discussing proprietary technology vs open-source approaches, AMD is more aligned with open-source principles across its platforms. At the same time, NVIDIA combines its proprietary technologies with significant contributions to open-source projects and support for open-source software.
Comparative Analysis of Strategic Partnership
AMD and NVIDIA have strong partnerships with major manufacturers, which is crucial for their future success in the rapidly evolving AI and HPC landscapes. For instance, AMD collaborates extensively with Dell, Lenovo, and Supermicro. NVIDIA also partners with Dell, HPE, and Lenovo and has extensive partnerships with cloud providers and OEMs. These collaborations give NVIDIA a strategic advantage, ensuring its AI hardware is widely accessible and integrated into various platforms and solutions.
Key Partnership: TSMC
TSMC [TSM] is recognized globally as the leading high-end chip manufacturer, which is especially crucial for innovative AI chips. AMD is poised to become TSMC's second-largest customer after Apple. This strong position allows AMD to negotiate favorable terms and secure priority access to advanced 3nm and 4nm technologies. NVIDIA also relies heavily on TSMC for its high-performance AI products like the A100 and H100 GPUs, essential for AI and data center applications. Additionally, NVIDIA employs a diversified manufacturing strategy, utilizing Samsung Foundry for specific needs, such as advanced 2.5D packaging for its AI GPUs, highlighting the strategic depth of its manufacturing partnerships.
The Magic Touch
NVIDIA co-founder and CEO Jensen Huang has positioned himself as a key figure in the new industrial revolution driven by AI. His visit to Computex 2024 and his interactions with major players in Taiwan's AI supply chain strengthened NVIDIA’s chip demand, recognizing that the true risk lies in securing these components. Ultimately, it is a battle of securing AI chip production capabilities from TSMC and their suppliers. Huang's personal anecdotes and his praise of Taiwan as the ‘unsung hero’ of the computer industry have endeared him to his business partners. By infusing a sense of humanity into the AI era, he sets a strong foundation for future advancements.
Financial Performance Comparison
Further analysis and scrutiny of their financials and balance sheets are necessary to provide a more comprehensive view. This includes an assessment of their stock performance and future projections.
Looking at the balance sheet, both companies have strong financials with high total assets (NVIDIA: $65.728 billion as of 1/31/2024; AMD: $67.885 billion as of 12/31/2023) and shareholder’s equity (NVIDIA: $42.978 billion; AMD: $55.892 billion), indicating their financial stability. NVIDIA has higher working capital ($33.714 billion) than AMD ($10.079 billion), which may provide more flexibility in its operations and investments. The company's strategic investments in AI and HPC capabilities have positioned it well for future growth. At the end of 2023, NVIDIA boasts substantial financial strength, with $13 billion in cash and $6.9 billion in debt. AMD has a lower total debt ($3.003 billion) than NVIDIA ($10.828 billion), which could be considered a lower financial risk.
Examining the stock market metrics, AMD has a Price-to-Earnings (PE) Ratio of 240.83 and a Price-to-Sales (PS) Ratio of 11.75. AMD's Asset Turnover Ratio, which measures the efficiency of asset use in generating sales, stands at 0.34, indicating that for every dollar of assets, AMD generated $0.34 in revenue. In contrast, NVIDIA's PS Ratio as of June 2024 is 48.052, and its Asset Turnover Ratio is 0.931, meaning that for every dollar of assets, NVIDIA generated $0.93 in revenue for the fiscal year ending January 31, 2024. In summary, NVIDIA appears to have better stock performance than AMD.
Dividends reflect a company’s robust financial condition and dedication to enhancing shareholder wealth, making them a crucial factor for investors to assess when considering the value of a company’s shares. Both companies have different strategies and perspectives on dividends. NVIDIA has increased its quarterly cash dividend by 150% to $0.01 per share after a ten-for-one forward stock split effective June 7, 2024. On the other hand, AMD does not pay dividends, as it focuses on reinvesting profits into the company to fuel growth and expansion.
Outlook
After examining both companies' financial stability and growth potential, we are confident that AMD and NVIDIA are well-positioned to capitalize on the growing demand for AI and HPC solutions. Recent significant orders further solidify their market positions, though potential risks, including regulatory scrutiny, remain.
Microsoft has announced plans to order more NVIDIA chips to power its expansive AI and cloud computing infrastructure. This indicates the strong demand for NVIDIA's GPUs in major data centers and cloud platforms. Additionally, Microsoft will increase its orders of AMD chips, demonstrating confidence in AMD's capabilities and highlighting its growing presence in AI and HPC markets.
Elon Musk's new venture, xAI, has committed to purchasing NVIDIA AI chips, further emphasizing NVIDIA's leadership in providing cutting-edge hardware for advanced AI research and applications. However, NVIDIA, along with other AI companies, is facing an anti-trust probe. This regulatory scrutiny could impact NVIDIA's operations and market strategy, posing risks to its market dominance and future growth. While AMD is not currently highlighted in the anti-trust probes to the same extent as NVIDIA, it remains vigilant about regulatory changes that could impact the broader AI industry.
The boxing match between these two AI heavyweights continues, and we eagerly anticipate seeing who will emerge as the winner of this exciting competition.
About the Author
Arthur Wang